Table of Contents
Plastic mulching transforms modern agriculture by offering farmers an efficient way to control weeds, retain soil moisture, and improve crop yields. This technique involves covering the soil with plastic sheets to create a controlled environment that enhances plant growth. It is widely used in vegetable farming, fruit production, and large-scale commercial agriculture.
Understanding Plastic Mulching
Plastic mulching is a farming technique where a thin plastic film is laid over the soil surface, with openings for crops to grow. This method helps regulate soil temperature, conserve water, prevent weed growth, and improve overall plant health.
Originally developed to extend growing seasons in temperate climates, plastic mulching is now used worldwide to increase productivity and efficiency in both small and large-scale farms. Farmers benefit from better soil moisture control, reduced need for herbicides, and improved plant growth conditions.
The Benefits of Plastic Mulching
Plastic mulching offers numerous advantages that make it a preferred choice among farmers:
Moisture Retention and Water Conservation
One of the biggest benefits of plastic mulching is its ability to reduce water evaporation. By covering the soil, the plastic sheet prevents direct sunlight from drying out the surface. This helps retain moisture, reducing the frequency of irrigation and making it an ideal solution for water-scarce regions.
Weed Suppression
Weeds compete with crops for nutrients, water, and sunlight, often reducing farm productivity. With plastic mulching, weed growth is significantly minimized because the mulch blocks sunlight from reaching the soil, preventing weed seeds from germinating. This reduces labour costs and the need for herbicides.
Temperature Regulation
Plastic mulch can help regulate soil temperature, making it warmer in cooler months and cooler in hot seasons. For example, black plastic mulch absorbs heat and warms the soil, allowing earlier planting and faster germination. On the other hand, reflective or white plastic mulch helps cool the soil in hot climates, reducing heat stress for crops.
Soil Erosion Control
In regions with heavy rainfall or strong winds, soil erosion can be a major challenge. Plastic mulching helps protect the soil from direct impact, reducing runoff and maintaining soil structure. This is particularly useful for sloped farmland.
Improved Crop Quality and Yield
With fewer weeds, consistent moisture, and better temperature regulation, crops grow healthier and stronger. Fruits and vegetables remain clean as they do not come into direct contact with the soil, reducing the risk of rot and disease. This leads to higher yields and better-quality produce, which fetches higher prices in the market.
Types of Plastic Mulch
Different types of plastic mulch are available, each suited to specific farming needs:
Black Plastic Mulch
This is the most common type of plastic mulch used in farming. It absorbs heat, warms the soil, and effectively suppresses weeds. Black plastic mulch is ideal for crops like tomatoes, peppers, and strawberries, which thrive in warm soil conditions.
White Plastic Mulch
Unlike black plastic, white plastic mulch reflects sunlight, keeping the soil cooler. It is used in regions with high temperatures where excessive soil heat can damage plant roots.
Silver or Metallic Plastic Mulch
This type of mulch is designed to repel insects such as aphids and whiteflies, which can harm crops. It also enhances light reflection, improving photosynthesis and promoting better crop growth.
Biodegradable Plastic Mulch
A sustainable alternative, biodegradable mulch is made from organic materials that break down naturally over time. This eliminates plastic waste and is an eco-friendly solution for farmers who want to maintain sustainable practices.
How to Install Plastic Mulch
Proper installation is essential for plastic mulching to be effective. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Soil Preparation
Before laying the plastic mulch, the soil must be properly prepared. This involves clearing weeds, loosening the soil, and applying any necessary fertilisers or compost. A well-prepared field ensures that the mulch is evenly distributed and effective.
Laying the Plastic Mulch
The plastic film should be carefully unrolled over the planting rows. The edges must be secured by burying them in the soil or using stakes to prevent the mulch from being blown away by the wind.
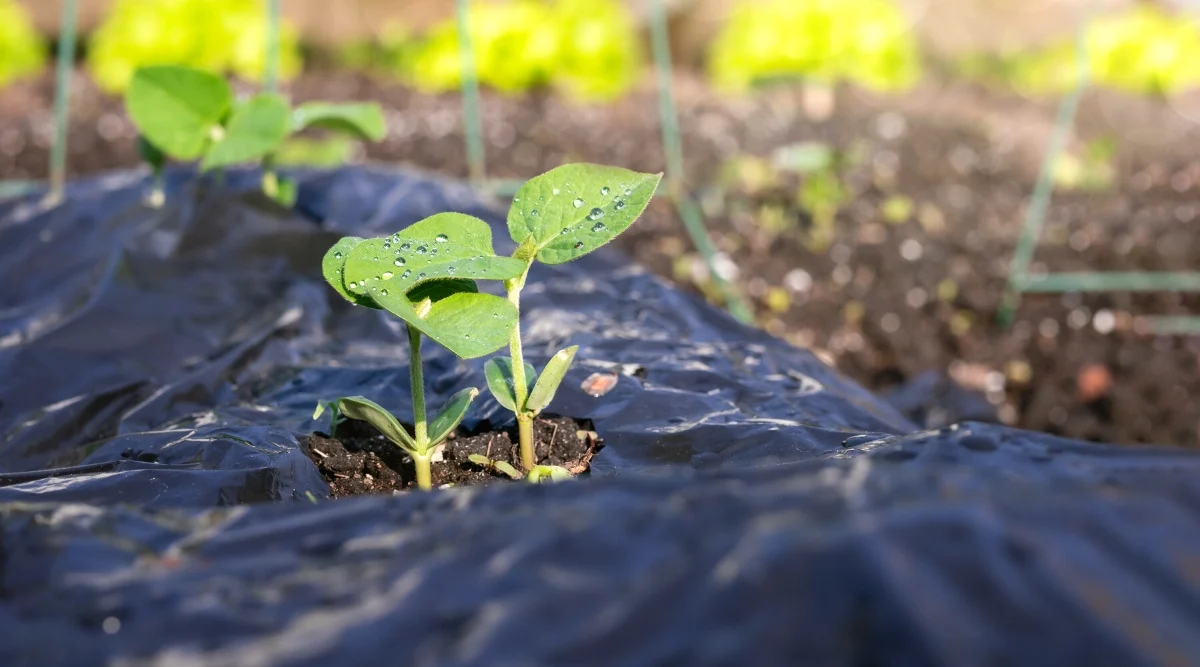
Creating Planting Holes
Small holes should be cut into the plastic mulch at the appropriate spacing for each crop. These openings allow plants to emerge while keeping the rest of the soil covered and protected.
Irrigation Setup
Drip irrigation is the most effective method for watering plants when using plastic mulch. Since the mulch prevents water from reaching the soil surface, drip irrigation ensures that water is delivered directly to the plant roots.
Best Crops for Plastic Mulching
Plastic mulching is particularly effective for certain types of crops, including:
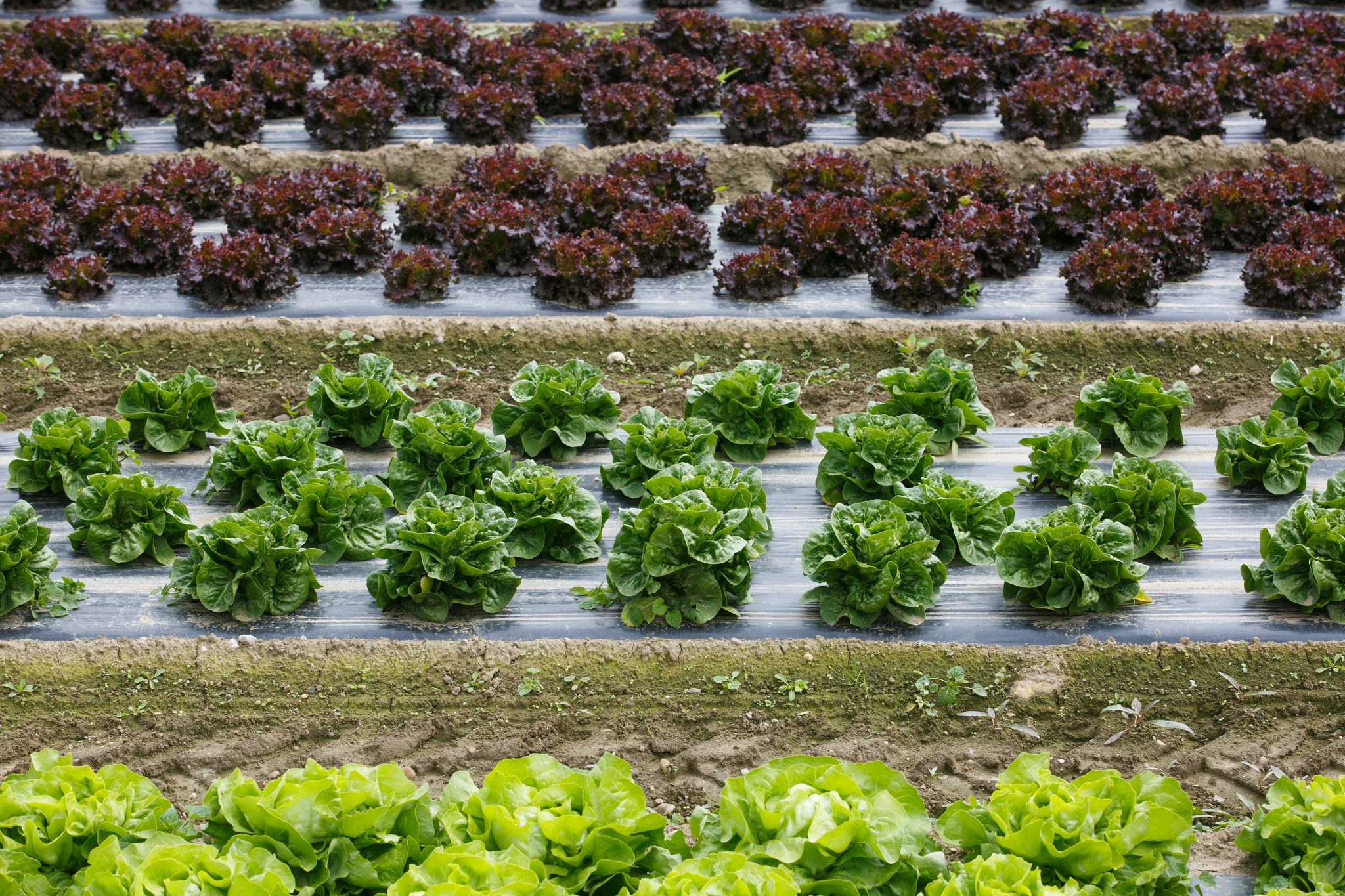
- Vegetables: Tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, melons, and lettuce.
- Fruits: Strawberries, watermelons, pineapples.
- Field Crops: Cotton, tobacco, and potatoes.
These crops benefit from the weed control, moisture retention, and temperature regulation that plastic mulch provides.
Challenges and Solutions in Plastic Mulching
While plastic mulching has many advantages, it also presents some challenges:
Plastic Waste Disposal
One of the biggest concerns with plastic mulching is the disposal of used plastic sheets. If not properly managed, plastic waste can contribute to environmental pollution. A solution is to use biodegradable plastic mulch or participate in recycling programs that collect and process used plastic mulch.
Initial Cost
Plastic mulching requires an initial investment in materials and installation. However, the long-term benefits, such as reduced labour and higher yields, often outweigh the costs.
Soil Overheating
In very hot climates, black plastic mulch can sometimes cause the soil to overheat, which can be harmful to plant roots. In such cases, white or silver mulch can be used to reflect sunlight and keep the soil cooler.