Table of Contents
Salt blocks are an essential resource for many animals, providing vital minerals that support their health and well-being. These compact, nutrient-rich blocks are particularly important for livestock, wildlife, and even some pets, ensuring they receive adequate sodium and trace minerals often lacking in their diets. Whether placed in a field for cattle or offered to a horse in a stable, salt blocks play a critical role in animal nutrition, promoting hydration, digestion, and overall vitality.
The Importance of Salt Blocks in Animal Diets
Animals, much like humans, require sodium and chloride, key components of salt, to maintain proper bodily functions. Sodium helps regulate fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions, while chloride supports digestion through the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. For herbivores such as cattle, sheep, and horses, natural forage often lacks sufficient sodium, making salt blocks a convenient and effective supplement. These blocks are typically made from compressed salt, sometimes enriched with trace minerals like zinc, copper, or selenium, which further enhance their nutritional value.
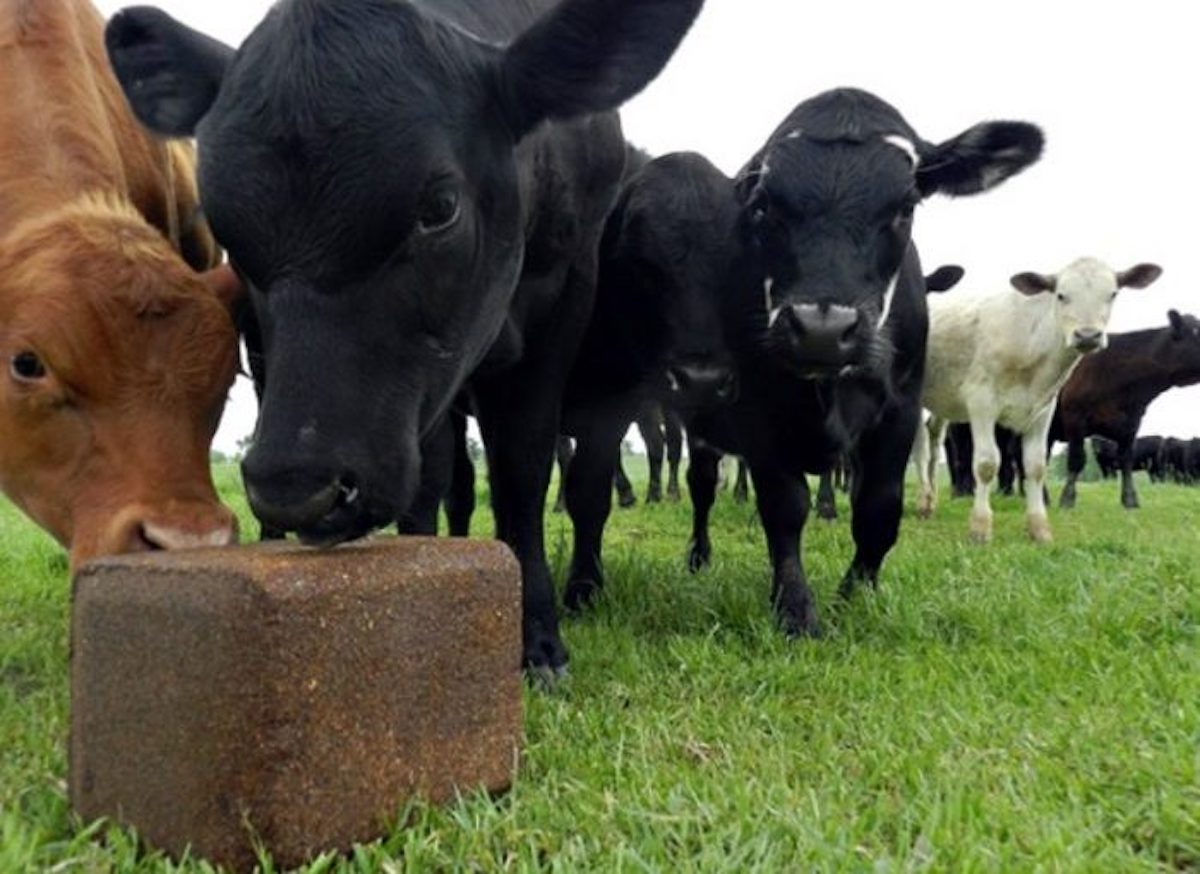
Farmers and animal caretakers rely on salt blocks to ensure their animals remain healthy, especially in environments where mineral deficiencies are common. For example, grazing animals in regions with nutrient-poor soil may not get enough sodium or other minerals from grass alone. By providing salt blocks, owners can prevent issues like reduced appetite, poor growth, or weakened immune systems, which can arise from mineral imbalances.
Types
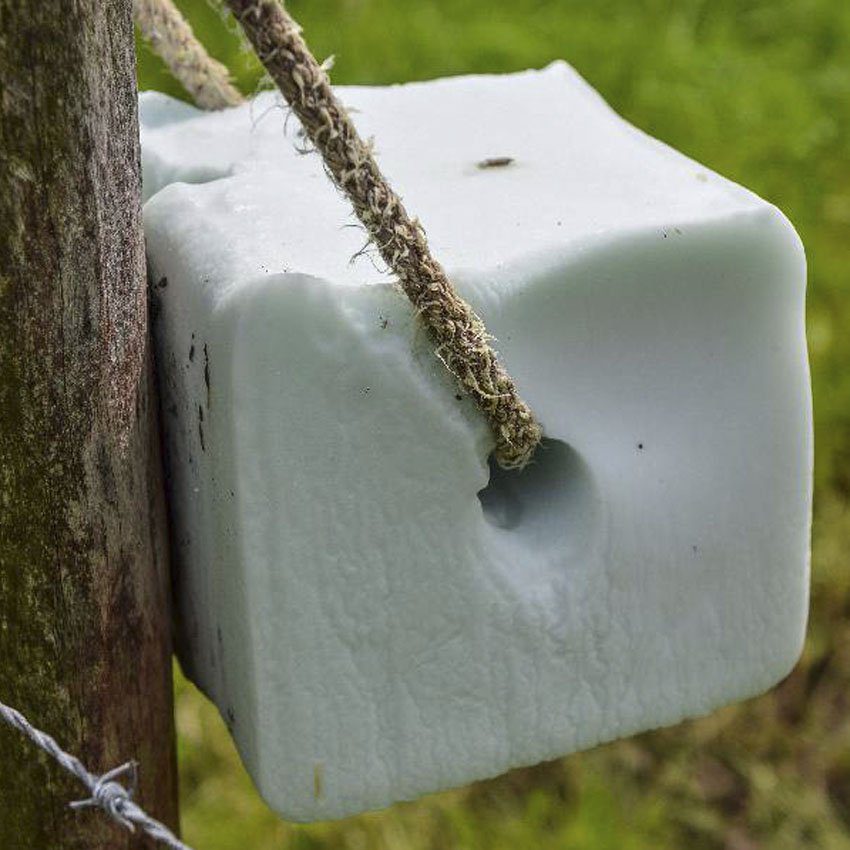
Salt blocks come in various forms, each tailored to specific animals and purposes. The most common type is the plain white salt block, made from pure sodium chloride. These are suitable for a wide range of animals, including cows, goats, and deer. Another popular option is the mineral-enriched salt block, often reddish-brown due to added nutrients like iron or iodine. These are particularly beneficial for livestock in areas where the soil lacks essential minerals.
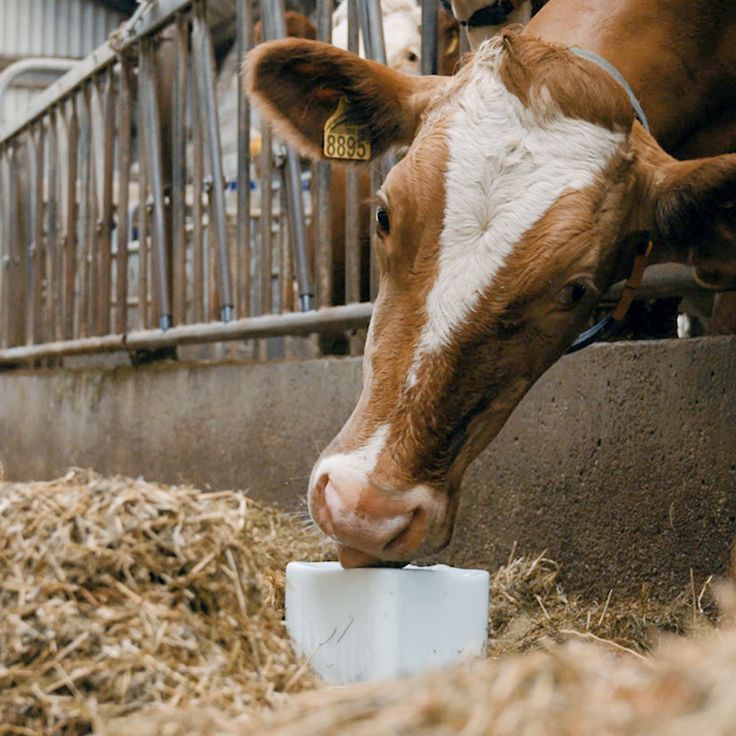
For horses, salt blocks are often smaller and designed to fit in a holder within a stable or paddock. Some blocks are even flavoured to encourage animals to lick them regularly. Himalayan salt blocks, prized for their natural pink hue and trace mineral content, have gained popularity for both livestock and pets like rabbits or hamsters. Each type of salt block serves the same fundamental purpose: delivering sodium and minerals in a form animals can easily access.
Benefits
One major advantage is their role in encouraging animals to drink water. Sodium intake stimulates thirst, which is crucial for preventing dehydration, especially in hot climates or during intensive work, such as when horses are ridden or cattle are herded. Adequate hydration supports kidney function and helps animals regulate body temperature.
They also promote healthy digestion. In ruminants like cows and sheep, sodium aids in saliva production, which is essential for breaking down fibrous plant material. Additionally, trace minerals in some salt blocks can improve coat quality, hoof strength, and reproductive health, making them a valuable tool for farmers aiming to maintain productive herds.
For wildlife, such as deer or elk, salt blocks placed in natural habitats can attract animals while supplementing their diet. Hunters and conservationists often use them to support local ecosystems, ensuring wild animals have access to nutrients that may be scarce in their environment.
Practical Considerations
While salt blocks are simple to use, there are a few considerations to ensure they’re effective. Placement is key. Blocks should be kept in a dry, accessible location to prevent them from dissolving in rain or becoming contaminated. For livestock, salt blocks are often placed in holders or troughs to keep them off the ground. Regular checks are needed to replace blocks as they’re consumed or weathered.
It’s also important to match the type of salt block to the animal’s needs. For instance, a dairy cow may require a mineral-enriched block to support milk production, while a pet rabbit might only need a small, plain salt block. Overconsumption is rarely an issue, as animals naturally regulate their intake based on need, but providing too many blocks in a confined space can lead to waste.
Challenges and Misconceptions
One common myth is that animals can become “addicted” to them. In reality, animals lick salt blocks to meet their physiological needs, not out of habit. Another concern is that salt blocks might harm animals by causing excessive thirst or mineral imbalances. When used correctly, however, salt blocks are safe and beneficial, with animals instinctively consuming only what they require.
Weather can pose a challenge, as rain can erode salt blocks, leading to waste. In wet climates, farmers may need to invest in covered feeders or opt for weather-resistant blocks. Additionally, not all animals need salt blocks year-round; those with access to naturally salty forage may require less supplementation.
BUY SALT BLOCK ON AFRIMASH: Brown Salt Licks (Salt Blocks | 5kg)